How To Install Os Over Lan
Summary :
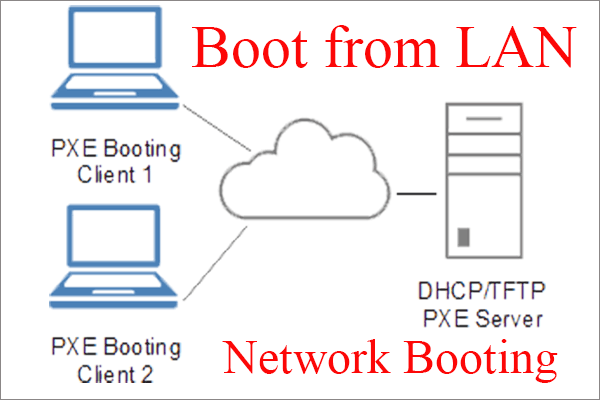
This commodity mainly introduces an unusual fashion to kick up a computer from LAN/network or remote computer/server/desktop/PC. It defines what kick from LAN is and how it works. As well, it uses an case based on MiniTool software. Continue reading for more than details!
Quick Navigation :
- What Does Boot from LAN Mean?
- Network Booting Use Case
- Hardware Support of Netboot
- Intel PXE Kick to LAN
- How to Boot from LAN?
- Boot from LAN with MiniTool ShadowMaker PXE
- How to Install Os Through Network Boot?
- Wake on LAN Kick
- User Comments
What Does Boot from LAN Mean?
Booting from LAN (Local Area Network), likewise known every bit booting from network, is a process that enables a computer to start up and load an operating system (OS) or other applications direct from the LAN without any local storage device such as CD-ROM, DVD-ROM, USB wink drive, or floppy deejay.
Tip: ROM refers to Read-Only Memory.
What Is Network Boot?
Network booting, shortened as netboot, is the process of booting up a estimator from a network instead of a local disk. This booting method can be applied to centrally managed computers (thin clients) like public machines in Cyberspace café or schools, diskless workstations, too as routers.
Network Booting Use Case
Network boot tin be used to centralize the management of hard drive storage, which supporters claim can reduce uppercase and maintenance expenses. It can also be applied in cluster computing, in which nodes may non accept local drives. In the late 1980s and early 1990s, network booting was used to salvage the cost of a hard drive for a decently sized hd would cost thousands of dollars, which is almost the price of a CPU.
Network booting is also used for unattended organisation installations. In such a situation, a network-booted helper system is used equally a platform to execute the script-driven, unattended installation of the intended Bone on the target computer. the implementations of that awarding for Windows and Mac Os 10 exist as Windows Deployment Service and NetInstall respectively.

This article tells you how to effectively solve the black screen boot error PXE-E61 Media test failure check cable using 7 different methods.
Hardware Back up of Netboot
Almost all modern desktop and laptop computers offering an option to boot from LAN in their BIOS or UEFI through PXE (Preboot Execution Surroundings). Postal service-1998 PowerPC (G3 – G5) Mac systems can also boot from their New World ROM firmware to a network deejay via NetBoot. Every bit for the older personal computers that have no network boot firmware, they can rely on a wink drive or floppy disk, which contains software, to kick from network.
Intel PXE Kick to LAN
On Intel architecture computers, network boot is enabled with the PXE standard. PXE extends the features of BIOS and so that information technology can run the software direct from the LAN. Nowadays, PXE support is so common that you can observe it in whatever modern machine that comes with an Ethernet jack called RJ45, which makes it possible to boot an Intel-based PC from the network without having to burn an EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Retentivity) on your network bill of fare like what you lot had to practice in the past.
How to enable PXE boot for Intel Desktop Boards? On Intel Desktop Boards that support the PXE, yous can set the network as a boot device. At present, let's see how to kick from onboard LAN.
- Printing F2 continuously when you power upward your machine until it enters its BIOS Setup.
- Navigate to the Boot menu.
- Enable Kick to Network.
- Press F10 to salvage changes and get out the BIOS setup.
- Restart your computer and press F12 during POST to boot from a remote server inside LAN.
Tip: To employ the F12 central during POST, the User Access Level in the Security menu of the BIOS Setup must be fix to Total.
How to Kick from LAN?
The process of network booting is like this. The initial software to be run is loaded from a server on the network. For IP networks, normally, this is done using the TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol). The server from which to load the initial software is often found past broadcasting a DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) or Bootstrap Protocol request.
Normally, that initial software isn't a full image of the Os to be loaded, but a small-scale network boot managing director programme like PXELINUX that can deploy a kick selection menu and so load the full image by invoking the respective 2d-phase bootloader.
Earlier IP became the primary Layer 3 protocol, IBM's RIPL (Remote Initial Program Load) and Novell's NCP (NetWare Cadre Protocol) were widely used to boot from Internet. Their client implementations also fit into smaller ROM than PXE. Technically, netbooting can exist practical over any of resource sharing or file transfer protocols. For case, NFS (Network File Arrangement) is preferred past BSD (Berkeley Software/Standard Distribution) variants.
If yous want to know what the PXE is and how to kick Windows in PXE, this mail is what y'all demand. What'southward more than, you can get other information well-nigh the PXE boot.
Side by side, allow'due south explain the BIOS boot process in item.
When the estimator powers on and starts running the operating system, it goes through a series of operations before information technology finally starts the OS. The system is a sophisticated boot program that takes total control over the PC. Yet, a kick program can too exist a very simple app such as a memory diagnostics tool.
Pace 1. Computer Powers on
The machine powers on afterwards you press the power button on the host case.
Stride ii. Hardware Initialization
So, the BIOS conducts an inventory of all the components in the reckoner like CPU, memory, and hard drives.
Step 3. Cocky-tests
Next, all the components detected by BIOS will go through a cocky-examination procedure to brand sure they are working properly. If i of the components fails and it is required for bones operation, your PC will brand a series of beeps and stop working. Just when all issues have been solved, the BIOS will movement on to the next step to discover additional option ROMs.
Footstep iv. Computer Stops
If your PC ends up in that state, it will either hang forever or turn itself off, which depends on how information technology entered that state and how your BIOS is configured to react when it comes across that state.
Pace v. Discover Built-in Devices and Option ROMs
During the process, the BIOS will detect all the extensions available, which are often embedded in the firmware of the BIOS or burned into an EEPROM or flash chip on ane of your add-on cards. Amongst those cards, y'all tin run across the prompt on the network cards assuasive you to decide which type of boot protocol it should support, PXE or RPL (Remote Program Load).
Usually, selection ROMs should do zero fancy at that point except initialize the hardware, run cocky-tests, and set up boot service (Bbs) entry signal. And, y'all will be permitted to select which boot service to try showtime by pressing a hotkey that varies from manufacturers. F12 is the most common i.
Step 6. Showtime the First Boot Service
Now, the application indicated by the boot service entry point is started. At this moment, command passes to the boot service that starts its discovery process for a boot program.
Step 7. Boot Service Discovers Boot Programme
Unlike kicking services await for the boot tools in different ways. As for the network menu using the PXE standard, information technology volition perform a DHCP request to observe its IP address and location of boot software. If a location is advertised, a TFTP request is performed to fetch the boot program, commonly referred to as a network boot program (NBP).
Step 8. Remove First Boot Service or Put Information technology at the Bottom of the Boot Listing
If the boot service fails to find a valid boot app, the boot service will go out, and control returns to the BIOS. The BIOS will cycle to the next boot service in its list. Whether the BIOS will remove the failed boot device or put it to the end of the list depends on BIOS vendors.
Step nine. Effigy out Additional Available Kicking Services
If in that location are more than boot services available, the side by side one in the kick list will exist started. If non, the computer will stop.
Step 10. Start Boot Plan
At present, the kick programme controls the computer completely. It will kickoff doing whatever it's supposed to do. Once the boot program has done all the tasks it should exercise, it will manus over the command to a system kernel. A boot programme that conducts that piece of work is known every bit a bootloader.
And so, the Bone kernel will perform a complete discovery of the hardware attached to the system and start doing whatsoever it is designed to do.
MiniTool ShadowMaker is a professional person and reliable fill-in software that also enables you to boot client computers within LAN from a host PC using its PXE feature. Let's come across how it works.
Free Download
1. Download, install, and launch MiniTool ShadowMaker on the host car.
2. If information technology asks for purchase, click the Keep Trial option in the upper correct.
3. Then, information technology volition enter into its main user interface (UI). There, move to the Tools tab from the summit bill of fare.
four. In the Tools tab, select PXE.
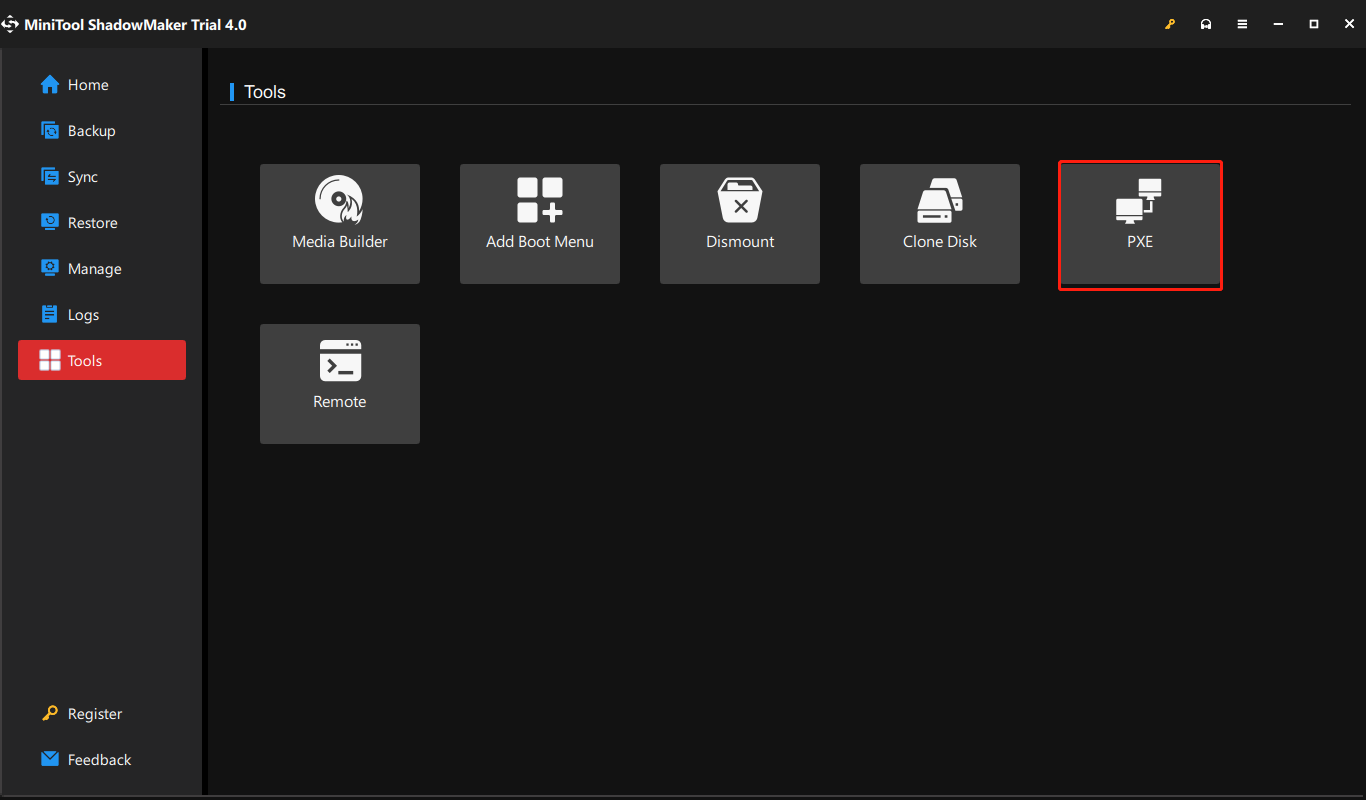
v. In the next PXE Customer window, click the Start push button to start the PXE service.

6. You tin use the Settings push to specify the beginning IP address of the clients, how many clients tin be started from this boot service, the router IP, too equally the mask.
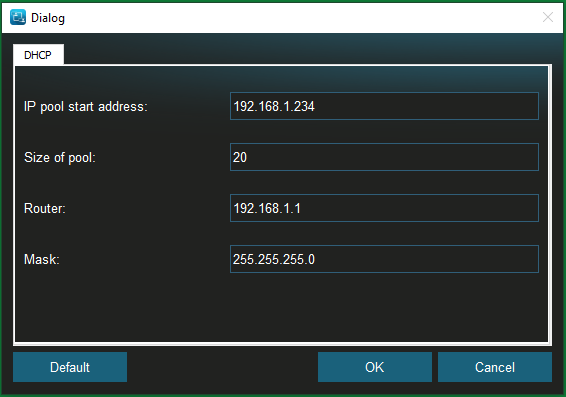
7. Boot the client computer within the same LAN as the host car into BIOS and change its first boot service to PXE.
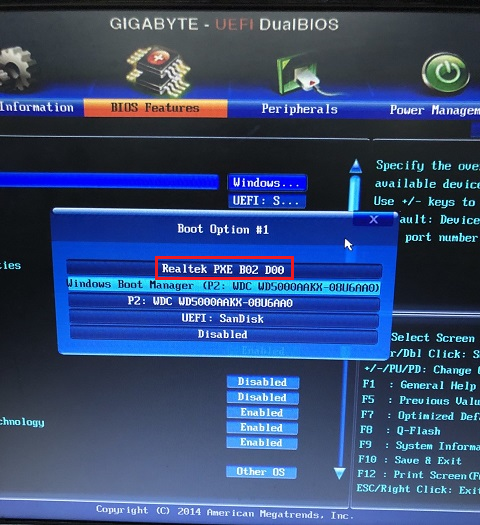
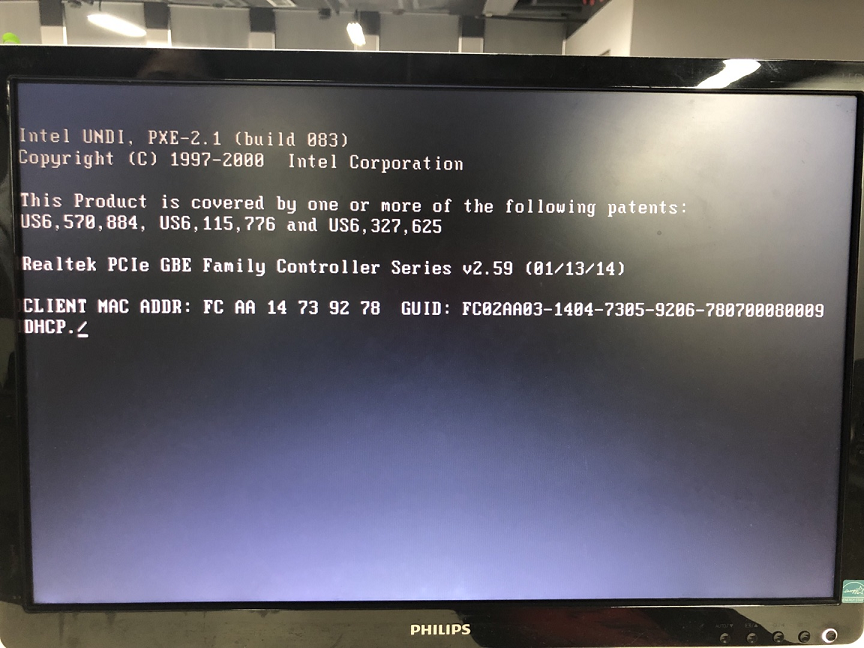
viii. Reboot the client and it will commencement upward from LAN into the Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE) with MiniTool ShadowMaker included. And, it will automatically open MiniTool ShadowMaker after the timer counts down for 15 seconds. If you don't desire to launch the program, just click Cancel.
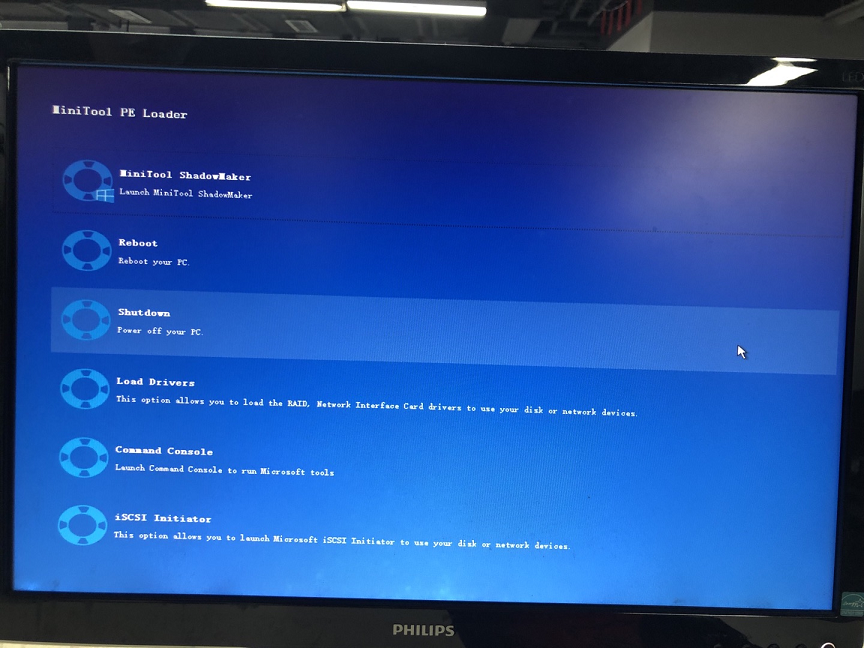
9. Finally, you will arrive at the screen of the MiniTool PE Loader. There, you can launch MiniTool ShadowMaker, reboot your PC, turn off your PC, load drivers, apply the command console, and launch Microsoft iSCSI Initiator.
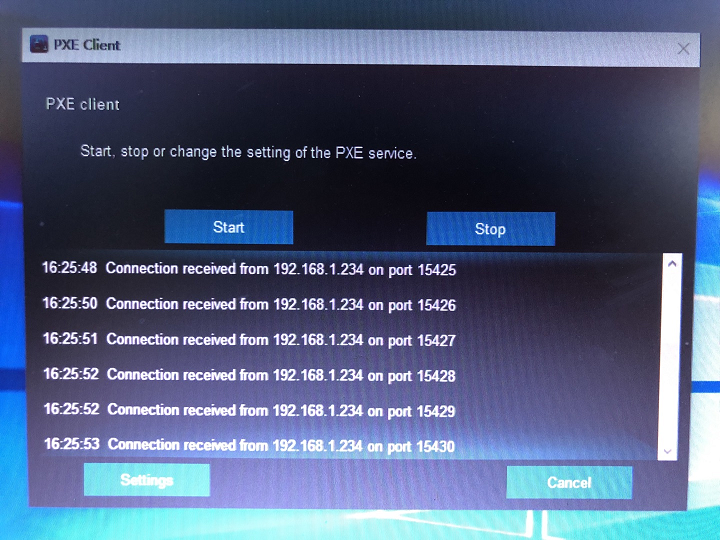
x. Go to boot up other clients with the same teaching starting from step seven.
Render to the host reckoner, yous will meet how many clients have been booted up from this PXE service and their temporary IP addresses and ports.
How to Install OS Through Network Boot?
If the customer computer is blank mental or its original system is damaged, you can rely on network booting to install systems on it. The following guide applies to Windows 7/8/8.one/ten/xi.
If you have a Windows installation media, merely connect it to the target client computer, boot it from LAN, and install the operating organisation on the client with the installation media.
If you don't have an installation disk, y'all can create a system backup with MiniTool ShadowMaker on a working computer and salve the fill-in epitome into a portable deejay. Then, connect the portable deejay to the client and boot upwards the customer with the MiniTool ShadowMaker PXE service post-obit the steps above. Finally, on the destination client, restore the system to its hard disk using the Universal Restore utility of MiniTool ShadowMaker.
Gratis Download
Wake on LAN Kicking
Wake-on-LAN (WoL) is an Ethernet or Token Band computer networking standard that enables a calculator to be awakened or turned on by a network bulletin. typically, the message is sent to the target figurer by a program executed on a device connected to the same LAN. Information technology is also possible to initiate the message from another network using subnet-directed broadcasts on a WoL gateway service.
Equivalent terms include wake up on LAN, power upwardly past LAN, ability on by LAN, resume on LAN, resume past LAN, remote wake-up, and wake on WAN (Wide Area Network). If the PC being awakened is communicating via Wi-Fi, a supplementary standard called Wake on Wireless LAN (WoWLAN) must exist employed.
Both WoL and WoWLAN standards are commonly supplemented past vendors to offer protocol-transparent on-demand services such as the Apple Bonjour wake-on-demand (Sleep Proxy) function.
Related article: How to Enable Wake-on-LAN in Windows 10?
Source: https://www.minitool.com/backup-tips/boot-from-lan.html
Posted by: fraziersyclee.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Install Os Over Lan"
Post a Comment